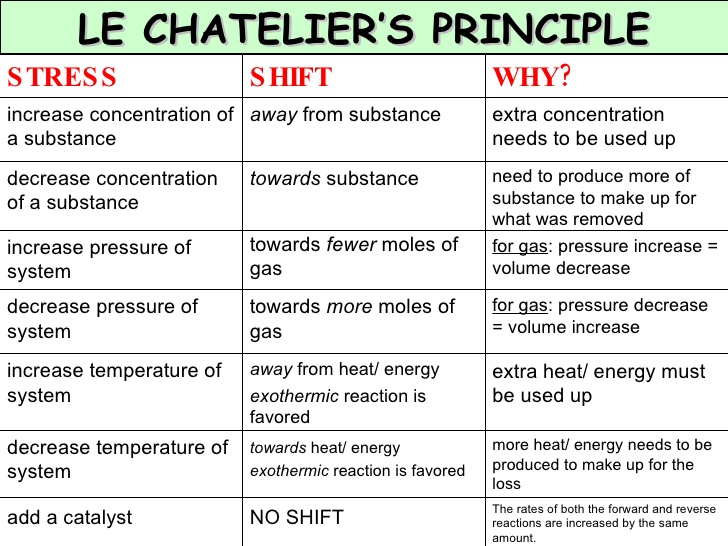
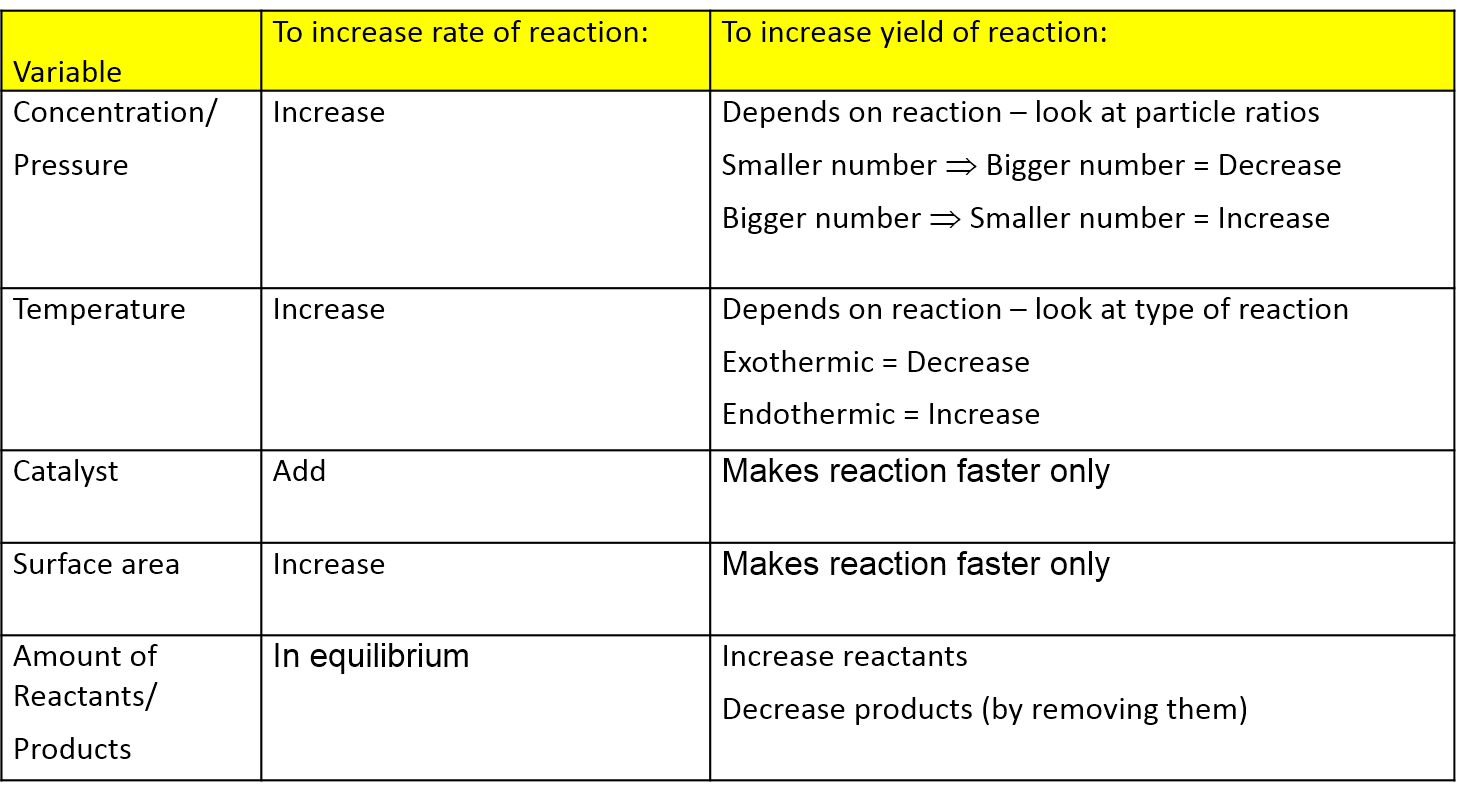
The generalization is known as LeChatelier's principle It may stated as "Change in any of the factors that determine the equilibrium conditions of a system will shift the equilibrium in such a manner to reduce or to counteract the effect of the change" The principle is very helpful in predicting qualitatively the effect of change in concentration, pressure or temperature on aOther articles where Le Chatelier's principle is discussed HenryLouis Le Chatelier who is best known for Le Chatelier's principle, which makes it possible to predict the effect a change of conditions (such as temperature, pressure, or concentration of reaction components) will have on a chemical reaction His principle proved invaluable in the chemical industry for developing theThe first green replacement lab that I implemented in my classroom was Beyond Benign's Equilibrium/Le Chatelier's Principle lab Traditional Le Châtelier's Principle experiments Le Châtelier's Principle is a favorite topic of my students because of the dramatic colors involved in the reactions The qualitative observations of the color changes allow students to predict and
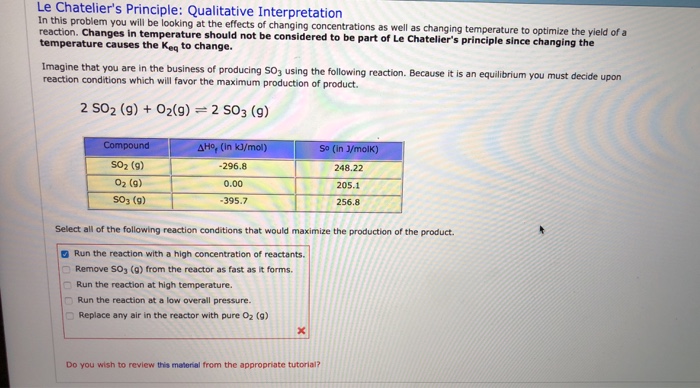
Solved Le Chatelier S Principle Qualitative Interpretati Chegg Com
Change in temperature le chatelier's principle
Change in temperature le chatelier's principle-19/10/18 · For purposes of applying Le Chatelier's principle, heat (q) may be viewed as a reactant Raising the temperature of the system is akin to increasing the amount of a reactant, and so the equilibrium will shift to the right Lowering the system temperature will likewise cause the equilibrium to shift left For exothermic processes, heat is viewed as a product of the reactionLe Chatelier's principle tells us the reaction will reachieve equilibrium by shifting to counteract this change Since the change we made was to increase the pressures the reaction will shift in such a way to decrease the pressures This can be achieved by moving towards the side of the reaction with fewer gas molecules Two key ideas to note First, this is only an effect for reactions that
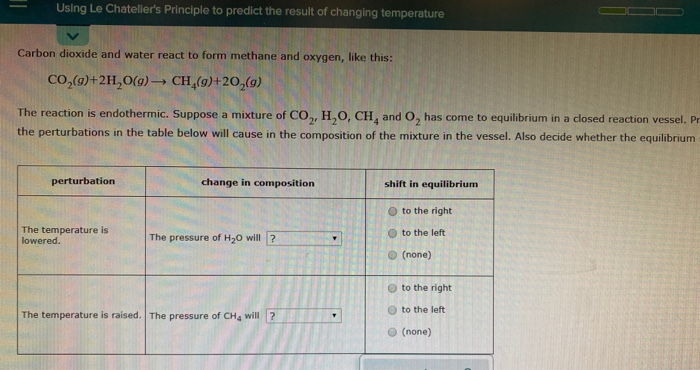


Solved Using Le Chatelier S Principle To Predict The Resu Chegg Com
According to Le Chatelier's Principle, the position of equilibrium moves in such a way as to tend to undo the change that you have made If you increase the temperature, the position of equilibrium will move in such a way as to reduce the temperature again It will do that by favouring the reaction which absorbs heat0 effect of temperature on position of equilibrium 12 Is there a reason for the mathematical form of the equilibrium constant?25/12/ · According to le chatelier's principle, the effect of concentration, temperature and pressure changes on the equilibrium of this reaction is as follows – Synthesis is increased by increasing the concentration of the reactants Synthesis will be higher at higher temperatures Pressure change has no effect
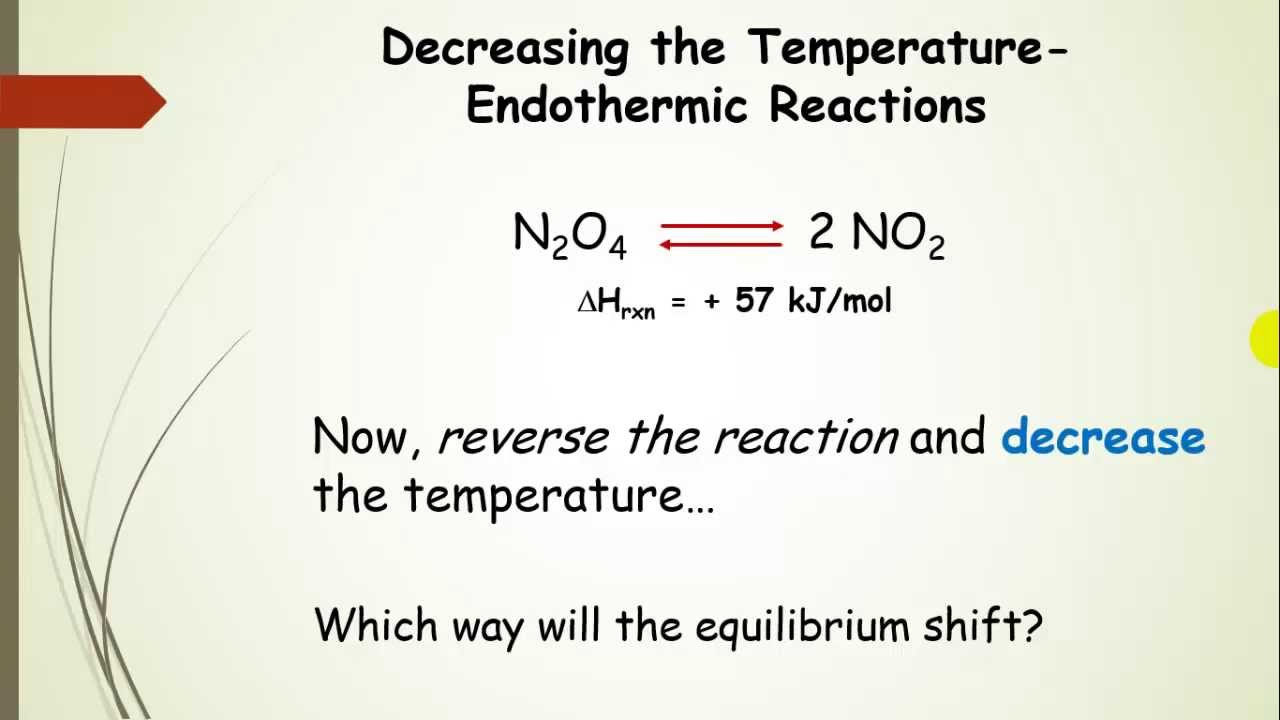
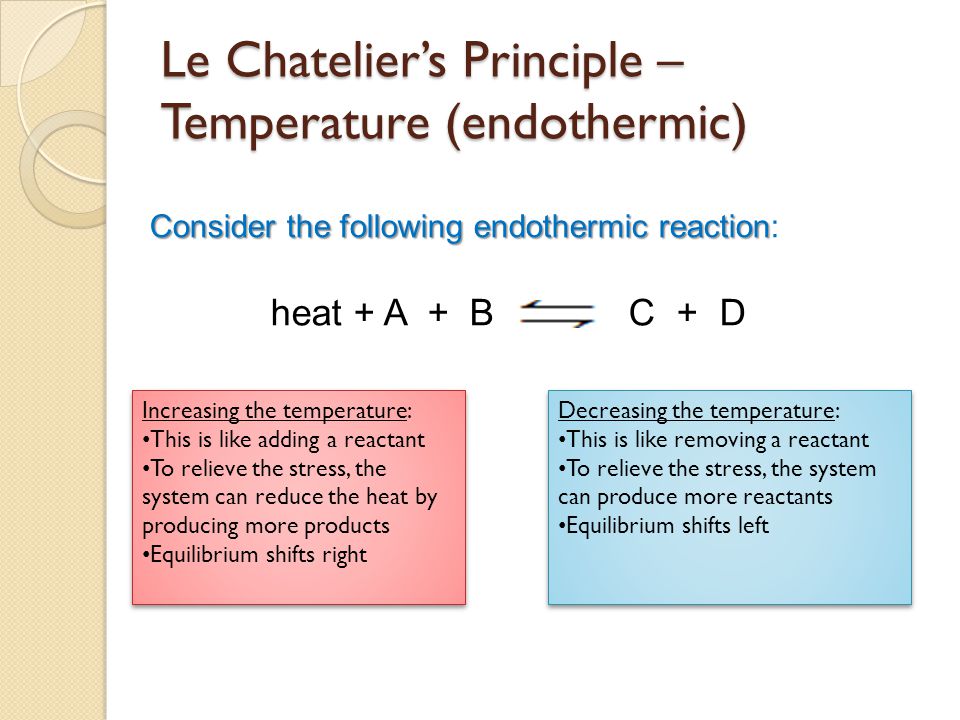
Le Chatelier's Principle "When a reversible reaction is in equilibrium and you make a change, it will do what it can to oppose that change" This is used to predict changes to the position of equilibrium when there are changes in temperature or pressureEffect of change in temperature The reversible reaction N 2 O 4 (g) ⇌ 2NO 2 (g) is endothermic, so the equilibrium position can be shifted by changing the temperature When heat is added and the temperature increases, the reaction shifts to the right and the flask turns reddish brown due to an increase in NO 2 This demonstrates Le Chatelier's principle the equilibrium shifts in theDr Shields discusses how to determine the direction the equilibrium will shift upon a temperature change based on the sign of the reaction enthalpy (H) Ge
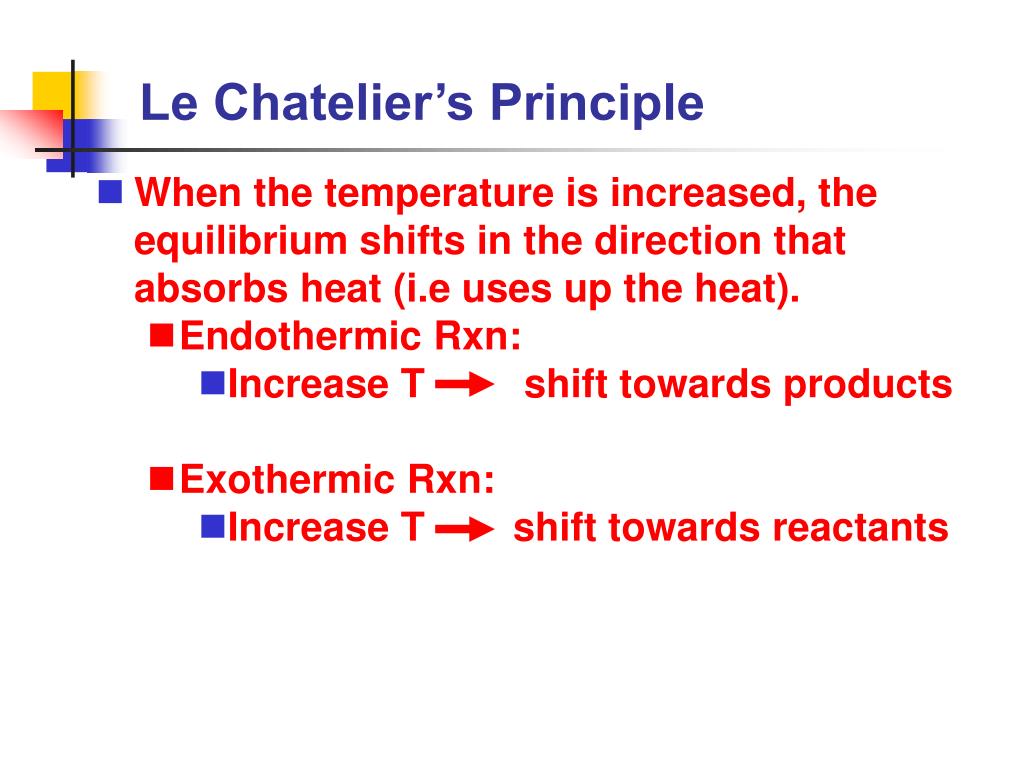
Le Chatelier's Principle • Le Chatelier's Principle is very useful in determining how the position of equilibrium can be changed to ensure more product is formed •Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system is at equilibrium and the temperature, pressure or concentrations of the species are changed, the reaction will proceed in such a direction as to oppose this changeApplying Le Châtelier's principle to determine optimum conditions The pressure In the reaction, N2(g) 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) notice that there are 4 molecules on the lefthand side of the equation, but only 2 on the right According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if you increase the pressure the system will respond by favouring the reaction which produces fewer moleculesLe Chatelier's Principle Le Châtelier's Principle states that if you change the conditions of an equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that minimizes the effects of whatever it is you did In other words picture equilibria is like obnoxious little kids For example, if you yell at a little kid, the kid will change his behaviour to minimize your yelling Likewise, if you change the



Solved Using Le Chatelier S Principle To Predict The Resu Chegg Com
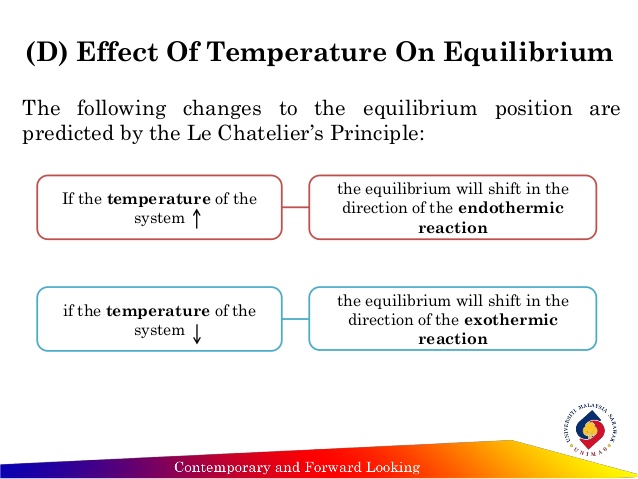


Question Cc8dd Socratic
Chatelier proposed one of the central concepts of chemical equilibria Le Chatelier's principlecan be stated as follows A change in one of the variables that describe a system at equilibrium produces a shift in the positionLe Chatelier's Principle The Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change of conditions, reactions occur in the system that tend to counteract the imposed change In other words, the system tends to react in a way that restores the equilibrium When the imposed stress is an increase or a decrease in pressureChanges in Temperature In an endothermic reaction, energy can be considered as a reactant of the reaction In an exothermic reaction, energy can be considered as a product of the reaction Le Chatelier's Principle predicts that the equilibrium position will shift in order to consume more heat if the reaction mixture is heated (that is, the endothermic reaction is favoured when the reaction



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Temperature Sl Youtube
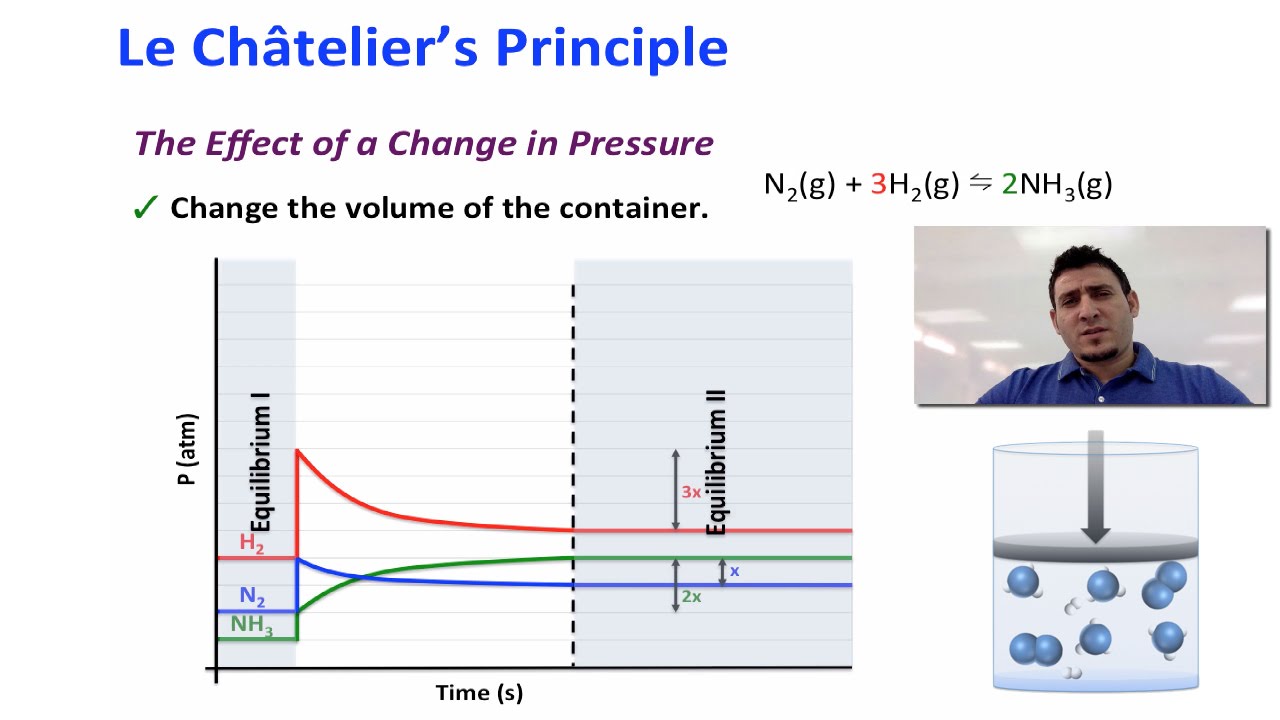


Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Youtube
16/11/ · Le Chatelier's principle as related to temperature changes can be illustrated easily be the reaction in which dinitrogen tetroxide is in equilibrium with nitrogen dioxide N 2O 4(g) heat ⇌ 2NO 2(g) Dinitrogen tetroxide (N 2O 4) is colorless, while nitrogen dioxide (NO 2)By Le Chatelier's principle, the system will act to consume some of the reactants to reduce the rate of collision and also the forward reaction rate Concentration of product will increase which increases the rate of reverse reaction Equilibrium is reached when forward reaction rate equals reverse reaction rateChanging the temperature In a reversible reaction, if the reaction is exothermic in one direction, it is endothermic in the other direction If the temperature is increased, the equilibrium



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Pressure Sl Youtube



The Position Of Equilibrium Topic 7 2 Equilibrium
02/11/19 · Le Chatelier′s Principle is the principle when a stress is applied to a chemical system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to relieve the stress In other words, it can be used to predict the direction of a chemical reaction in response to a change in conditions of temperature, concentration, volume, or pressureLe Chatelier's principle describes how a system atequilibrium reacts to changes (stresses) in system conditions It states that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temperature, pressure, or one of the components concentration, the system will transfer its equilibrium place to counteract the outcome of the disturbance13/08/19 · Le chatelier principle definition Le Chatelier principle predicts the effect on the system at chemical equilibrium when some of the factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration changeTherefore, how the system behaves in chemistry or chemical science if any of these parameters of the system be altered was predict by Le Chatelier in 15 and Braun in
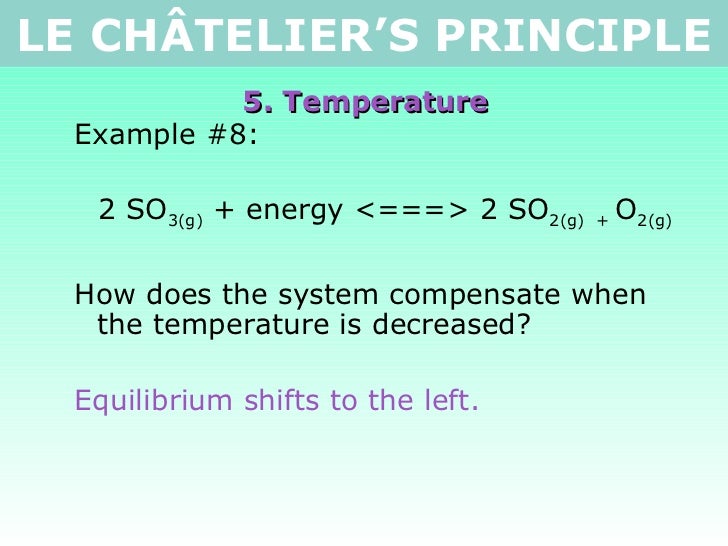


Tang 02 Le Chatelier S Principle 2



Le Chatelier S Principle Analytical Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
Le Chatelier's Principle Prediction of Response to Stress 2NO 2 (g) N 2 O 4 (g) energy Increase T Increase Decrease Decrease Since NO 2 is reddishbrown in color, the container will become much darker brown, as shown in the above image for the reaction at 100 o C Exactly the opposite will happen if we decrease the temperature Use le Châtelier's principle by applying theVolume and pressure changes will disturb equilibrium if the number of moles of gas is different on the reactant and product sides of the reaction The system's response to these disturbances is described by Le Châtelier's principle The system will respond in a wayThis video is about Le Chatelier's Principle changes in temperature



Explaining Le Chatelier S Principle Lechateliers



Le Chatelier S Principle
Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Saturated Solutions Solubility tables like the one above, tell us the maximum mass of solute that will dissolve in a given mass of solvent under certain conditions Typically, the conditions are a temperature of 25 o C and a pressure of 1013 kPa (1 atm) Let's see what happens when we change either of these conditions02/04/ · Thus the effect of change of temperature on the two reactions is different By LeChatelier's principle for an exothermic reaction at equilibrium lowering of temperature will favour the forward reaction And for an endothermic reaction, an increase in temperature will favour the forward reaction Effect of the Catalyst on the Chemical Equilibrium The catalyst is a substanceLe Chatelier's principle states that when a chemical system is at equilibrium, any change in concentration, temperature, volume, or partial pressure, will cause a shift in the equilibrium to counteract the imposed change A new equilibrium is therefore created



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide



Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Change Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Principles
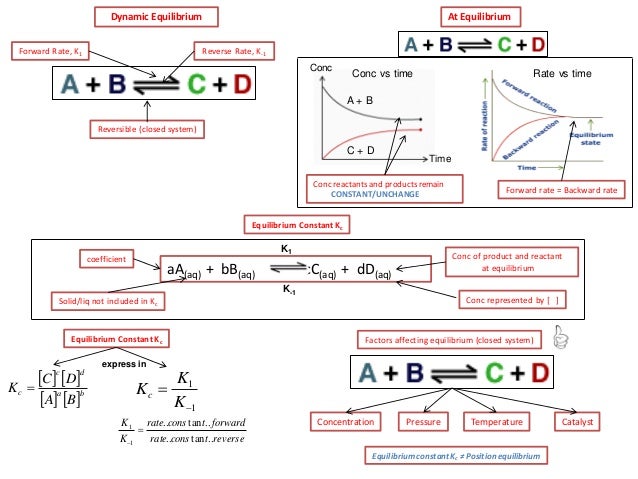
Le Châtelier's principle Any change that occurs in a system at chemical equilibrium causes an adjustment in the concentrations of reactant (s) or product (s) that reestablishes the equilibriumLe Chatelier's Principle helps to predict what effect a change in temperature, concentration or pressure will have on the position of the equilibrium in a chemical reaction This is very important, particularly in industrial applications, where yields must be accurately predicted and maximised \(\color{darkgreen}{\textbf{\Large Le Chatelier's Principle}}\) When an external stress (changeLe Chatelier's principle is an observation about chemical equilibria of reactions It states that changes in the temperature, pressure, volume, or concentration of a system will result in predictable and opposing changes in the system in order to achieve a new equilibrium state
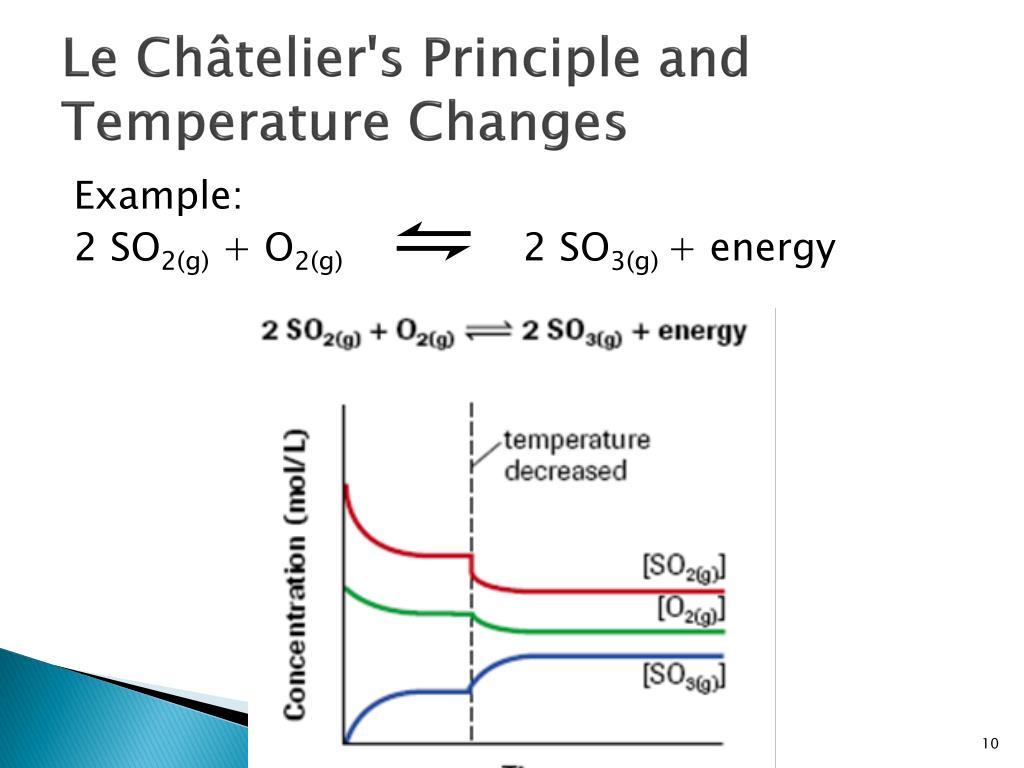


Ppt Chemical Systems And Equilibrium Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts
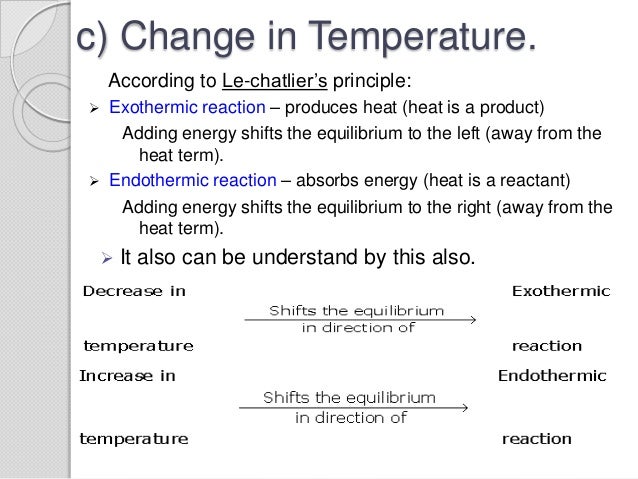
Changing the temperature of a system at equilibrium has a different effect A change in temperature actually changes the value of the equilibrium constant However, we can qualitatively predict the effect of the temperature change by treating it as a stress on the system and applying Le Chatelier's principle12 Derivation of van 't Hoff equation for temperature dependence of equilibrium constant 1 Why is the dissolution of AgCl considered endothermic?EFFECT OF CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE The effect of temperature can be understood by using le Chatelier's principle as follows 1) Increase in the temperature of the system favors the endothermic reaction The increase in temperature increases the amount of heat in the system



Using Le Chatelier 39 S Principle To Predict The Result Of Changing Nitrogen Monoxide And Ozone React To Form Nitrogen Dioxide And Oxygen Like This The Reaction Is Exothermic Suppose A Mixtur Homeworklib
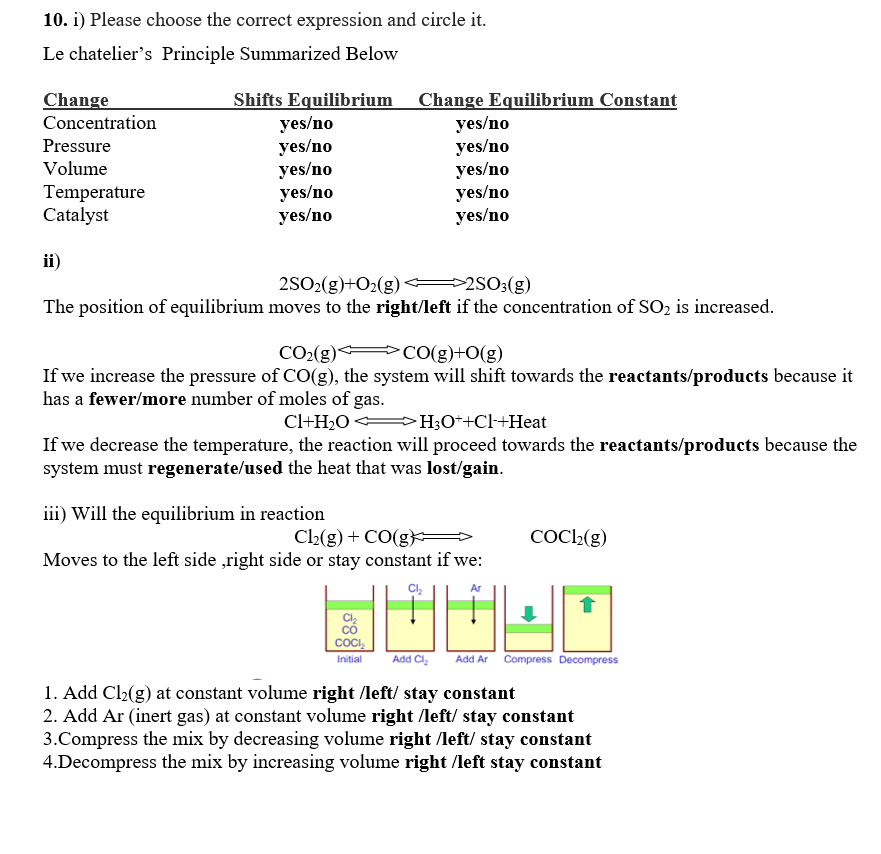


Answered 10 I Please Choose The Correct Bartleby
16/09/14 · Le Chatelier's principle addresses how an equilibrium shifts when the conditions of an equilibrium are changed The direction of shift can be predicted for changes in concentrations, temperature, or pressure Catalysts do not affect the position of an equilibrium;Le Chatelier's Principle on Change of Temperature As per the Van't Hoff equation, for an exothermic equilibrium, ∆H will be negative Increase of temperature shall decrease K 2 or decrease in temperature increases K 2 The opposite is true for an endothermic reactionIntroductionLe Chateliers principle statesThe position of the equilibrium of a system changes to minimise the effect of any imposed change in conditionsThis principle applies to any reaction that is in equilibriumThe effect of concentration changes on equilibriumChanging concentration of a reactant or product does not change the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, but it does



Pdf On Violations Of Le Chatelier S Principle For A Temperature Change In Small Systems Observed For Short Times



Energy Changes Reaction Rates And Equilibrium Thermodynamics Study
Le Chatelier's Principle is used for qualitative predictions of how a chemical system will respond to an alteration of its equilibrium conditions by means of change in temperature, pressure, or concentration of reactants and products The concept of this principle is closely related to the idea of chemical equilibria and equilibrium constantsLe Chatelier's principle Jump to navigation Jump to search Le Châtelier's Temperature If the temperature of whichever side is more endothermic as this will take in the excess energy as part of the products and so cancels the change of increased temperature Electromagnetism This principle is also shown by Lenz's law, which states that a changing magnetic flux will produce anLe Chatelier's principle predicts that the equilibrium will move to the right with an increase in temperature as the forward reaction is endothermic The brown colour intensifies The equilibrium constant, K p, has a value of 48 atm at 400 K (127 °C), and the equilibrium will lie almost completely over to the right at 140 °C Increasing the pressure moves the equilibrium to the left as



Explaining Le Chatelier S Principle Lechateliers



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula
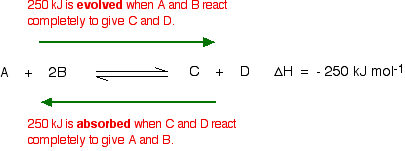
03/10/13 · Using Le Chatelier's Principle with a Change of Temperature For this, you need to know whether heat is given out or absorbed during the reaction Assume that our forward reaction is exothermic (heat is evolved) This shows that 250 kJ is evolved (hence the negative sign) when 1 mole of A reacts completely with 2 moles of BAccording to Lechatelier's principle a change in temperature is a stress on an equilibrium system If at equilibrium the temperature of system is changed the system will no longer at remain at equilibrium To restore equilibrium, the reaction will in either forward or backward directionLe Chatelier's principle is all about how a system will adjust itself when stress is put on it in order to reestablish equilibrium Equilibrium is when the rate of the forward and the reverse reactions are the same One stress taken into account is a change in concentration An increase in reactants or decrease in products results in an increase in the forward reaction rate, a shift to the



Question Video Main Disadvantage Of Increased Temperature In The Haber Process Nagwa



Le Chatelier S Principle
25/02/02 · Le Chatelier's principle applied to changes in concentration or pressure can be understood by giving K a constant value The effect of temperature on equilibria, however, involves a change in the equilibrium constant The dependence of KIn chemistry, Le Chatelier's principle, also called the Le ChatelierBraun principle, can be used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on a chemical equilibriumThe principle is named after Henry Louis Le Chatelier and Karl Ferdinand Braun who discovered it independently It can be summarized as If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature14/07/ · When an external stress (Change in temperature, pressure, concentration) is applied to a system in equilibrium The system will respond in a way which minimizing the effect of the change This is La Chatelier's principle Collision theory explain chemical reactions as successful collisions between reactant molecules, increasing the temperature or number of reactants



Chem 2 Chemical Equilibrium X Le Chatelier S Principle And Tempera



Answered 10 1 Please Choose The Corect Bartleby
Le Chatelier's principle tells you that changing the concentration of a substance causes the system to adjust to minimize the change in that substance The decomposition of carbonyl bromide provides an illustration If the three gases in the reaction were at equilibrium and you then increased the carbon monoxide concentration, some Br 2 would combine with added CO to produce COBr1 Shift of Equilibrium Related 5 EquilibriumThey help reactions achieve equilibrium faster



Lechatelier S Principle Ck 12 Foundation


Le Chatelier S Principle
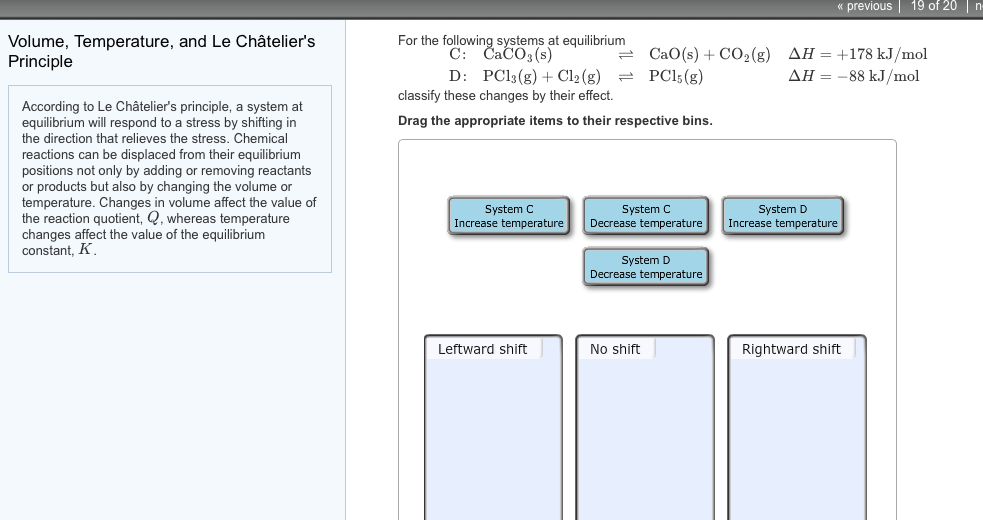
Why does Le Chatelier's principle work for temperature changes?Systems at equilibrium can be disturbed by changes to temperature, concentration, and, in some cases, volume and pressure;
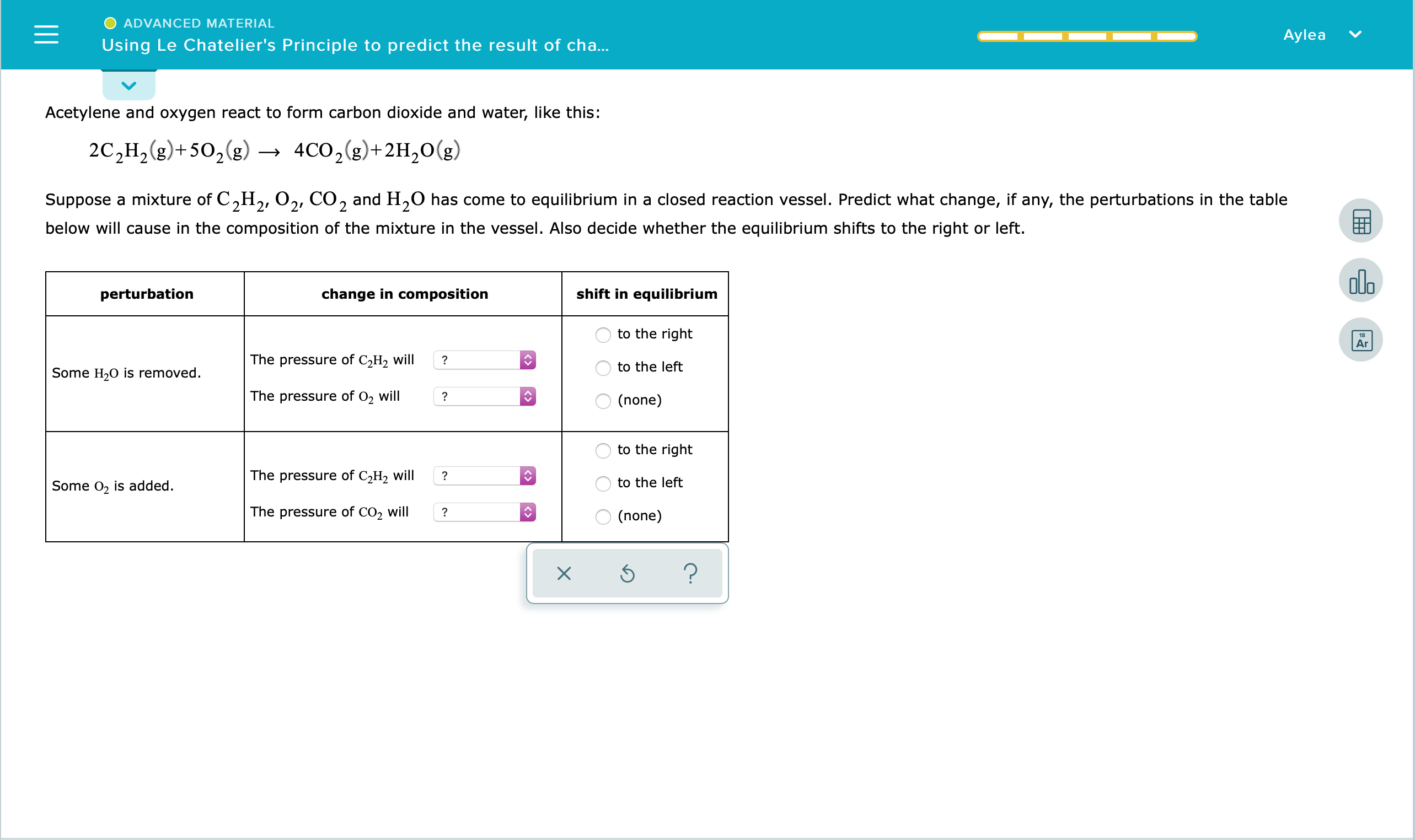


Answered Advanced Material Aylea Using Le Bartleby


Le Chatelier S Principle Qs Study
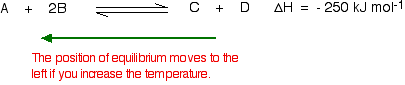


Le Chatelier S Principle



Increasing Temperature Le Chatelier Principle Get Images



Chemical Equilibrium And Le Chatelier S Principle



Solved Le Chatelier S Principle Qualitative Interpretati Chegg Com



Hcl Equilibrium


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



Ppt Le Chatelier S Principle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Chem 2 Chemical Equilibrium X Le Chatelier S Principle And Tempera



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide



Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula


Le Chateliers Principle Temperature Example Get Images


Ib Chemistry On Le Chatelier S Principle Haber And Contact Process



Le Chatelier S Principle
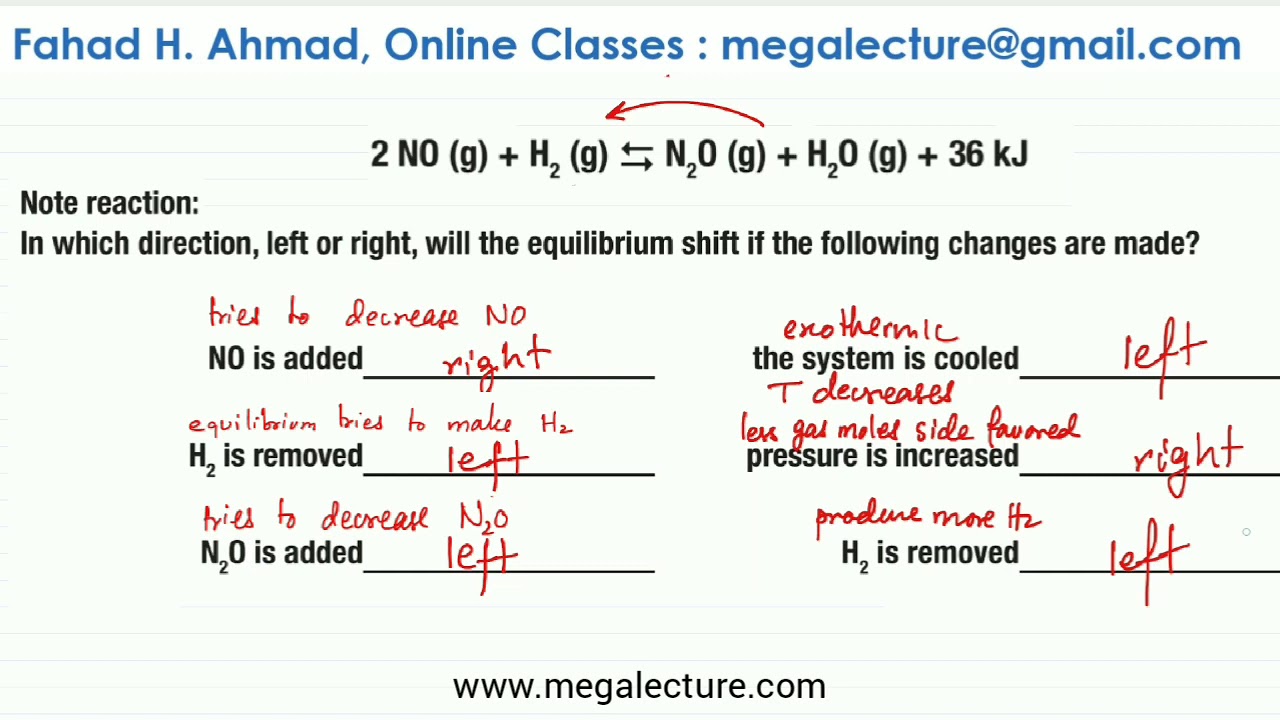


Le Chatelier S Principle Worksheet Solved Questions Youtube
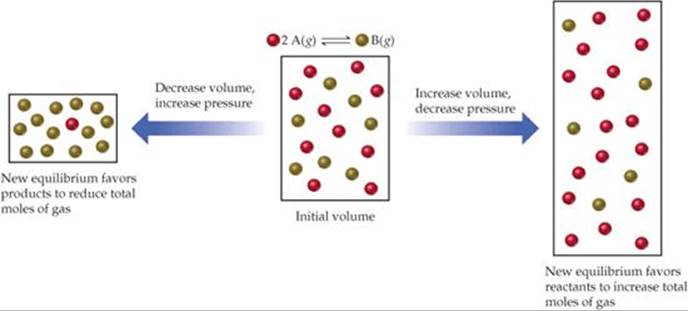


Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry The Central Science



Ppt Georgia Performance Standards Essential Questions Powerpoint Presentation Id
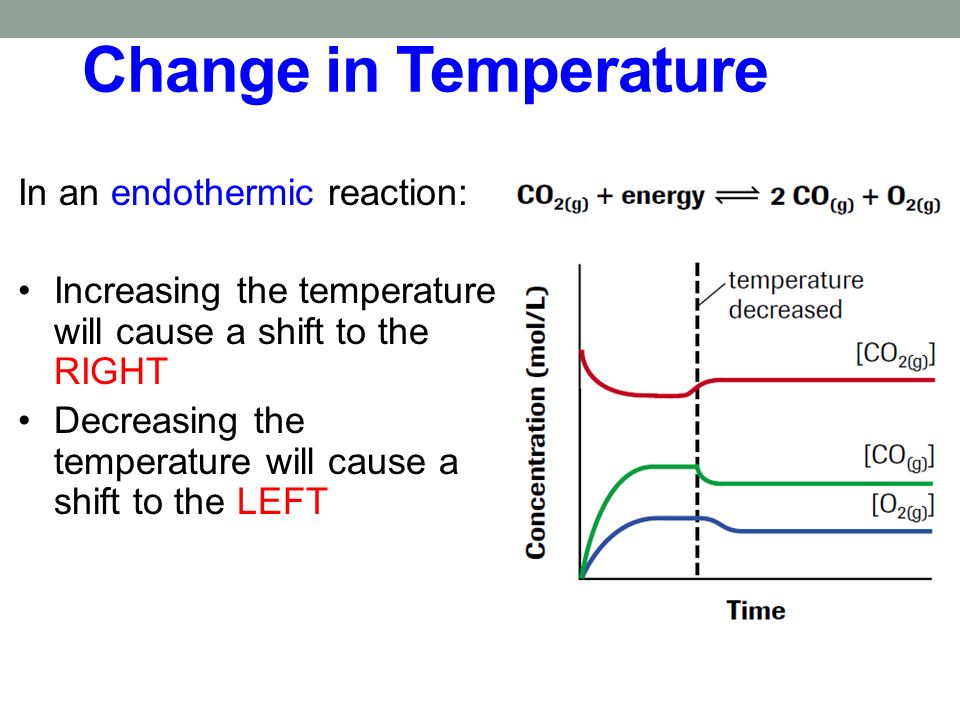


Le Chateliers Principle Temperature Change Get Images



Can Someone Please Check Over These Le Chatelier S Principle Questions I Also Need Help On 2 Of Them Since I M Not Sure How Temperature Affects The Amount Of Molecules Or How Adding



Chemistry Not Mystery Le Chatelier S Principle Concentration And Pressure Change



Learning Chemistry Easily Le Chatelier S Principle Effect Of Changing Temperature



15 Le Chatelier S Principle And Factors Affecting Equilibrium Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Reactions
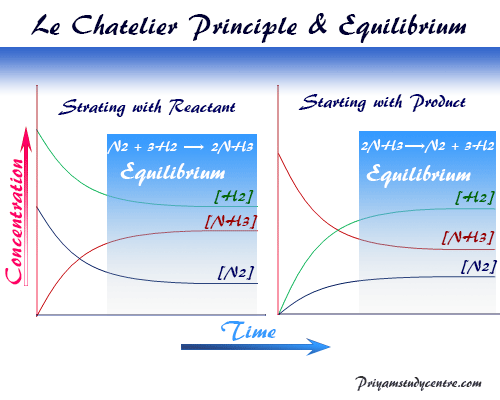


Le Chatelier Principle Definition Application Facts Priyamstudycentre



Le Chatelier S Principle And More Ppt Download



Chemistry Not Mystery Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Change



1 6 Chemical Equilibria And Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium As Secondary Science 4 All


Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Ganada



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Sl Youtube



Solved Consider The Following Reaction At Equilibrium Le Chegg Com


Le Chatelier S Principle


Solved Volume Temperature And Le Chatelier S Principle Chegg Com



Ppt Le Chatelier S Principle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Ganada



Effect Of The Change In Temperature On Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium Chemical


What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry Socratic



Le Chatelier Principle And Effect Of Temperature Pressure And Concentration On The Equilibrium Of A Ch Le Chatelier S Principle Teaching Chemistry Principles


Ppt Applications Of Equilibrium Constants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Le Chatelier S Principle Pv Changes On Gaseous Sytems Pt 9 Youtube



Chm 1046


10 1 Equilibrium Introduction And Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Honors Carroll



Le Chatelier Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Reactions



Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Video Online Download


Le Chatelier S Principle Le Chatelier S Principle Is An Idea About How A Reaction Mixture That Is At Equilibrium Will React When It Is Perturbed Away From Equilibrium This Is A General Idea That Can Help Us To Quickly Have Some Insight Into Chemical Equilibria And


Factor Effecting Chemical Equilibrium Fun Science



Le Chatelier Principle And Effect Of Temperature Pressure And Concentration On The Equilibrium Of A Ch Le Chatelier S Principle Teaching Chemistry Principles



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula


What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry



Chapter 13 Chemical Equilibrium 13 1 The Equilibrium


Le Chatelier S Principle Studocu



Equilibrium Tier 4 Apply Lechatelier S Principle To Predict The Qualitative Effects Of Changes Of Temperature Pressure And Concentration On The Position Ppt Download



Le Chatelier S Principle Applications Adichemistry


Le Chatelier S Principle Davidcalvin



Le Chateliers Principle Position Of The Equilibrium Equilibrium



1 6 Chemical Equilibria And Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium As Secondary Science 4 All



Reversible Reactions Equilibrium And Le Chatelier S Principle Compound Interest



Lechatelier S Principle And The Equilibrium Constant Ck 12 Foundation


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts
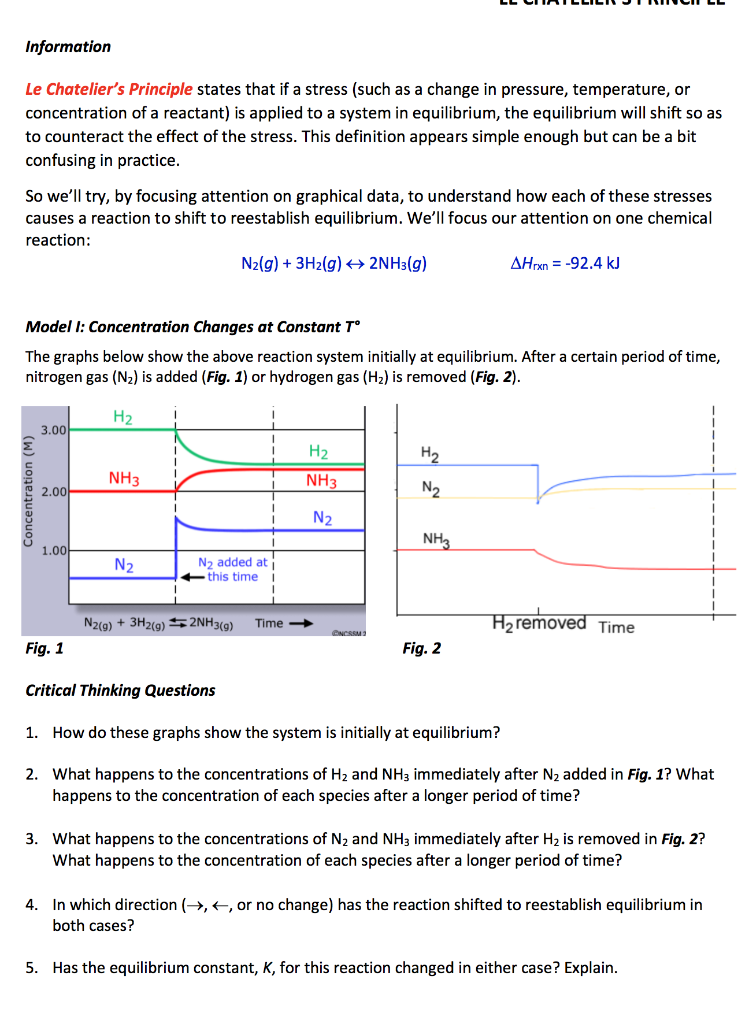


Solved Information Le Chatelier S Principle States That I Chegg Com



Le Chatelier S Principle Studypug


Equilibrium Dp Chemistry R Slider Ppt Video Online Download


Shifting Equilibria Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry For Majors



According To Le Chteliers Principle When A Chemical


Le Chatelier S Principle Vce Chemistry



9 6 Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Libretexts



Lesson Le Chatelier S Principle Nagwa



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Concentration Sl Youtube



Qualitative Changes In Equilibrium Systems Ppt Download



Lechatelier S Principle Equilibrium Lechatelier S Principle Co 2 Cao Caco 3 Chicken Breath Food Egg Shell I Wish I Had Sweat Glands As Temperature Ppt Download



Chemical Equilibrium I A State Of Dynamic Balance



Factors That Affect Chemical Equilibrium Boundless Chemistry


